Improving People, Animals, and Environment Health Through One Health Approach

Photo by Ivan Babydov on Pexels.
The world has been grappling with the COVID-19 pandemic for the last three years. The SARS-CoV-2 virus that put the world on a halt is a zoonotic disease, meaning that the virus can spread between animals and humans. Though the animal source of the virus is still yet to be determined, the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrates the fatality of zoonotic infectious disease and the need for a holistic solution.
The Interconnectedness
As fellow earth inhabitants, it is clear that the lives of humans, animals, and plants are intertwined, though often it’s us that benefit from them. Often, animals can act as an early warning of an emerging human illness, as they are also susceptible to some of our diseases. Apart from COVID-19, diseases such as Salmonella infection, rabies, and ebola are also considered infectious zoonotic diseases.
As the human population grows and animal habitats decline due to environmental degradation, humans and animals are forced to come in close contact more frequently. Furthermore, disruptions in the weather and environmental conditions also caused animals to be more vulnerable to contracting new diseases. With the chances for diseases to pass between animals and people getting higher, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) established a global campaign called One Health.
A Cross-Sectoral & Holistic Approach
One Health recognizes the interconnection between people, animals, plants, and their environments. Though the similarity between human and animal disease processes has been recognized since the 1800s, the One Health concept started to gain more recognition in recent years. In 2009, CDC established its One Health Office.
In short, the One Health approach seeks to improve the overall health of people, animals, and their shared environments. A healthy environment will affect the well-being of people and animals. Likewise, a healthy population signifies a good, habitable environment. It encourages cross-sectoral collaborations between human, animal, and environmental health experts to tackle issues such as zoonotic diseases, food safety and security, and environmental contamination.
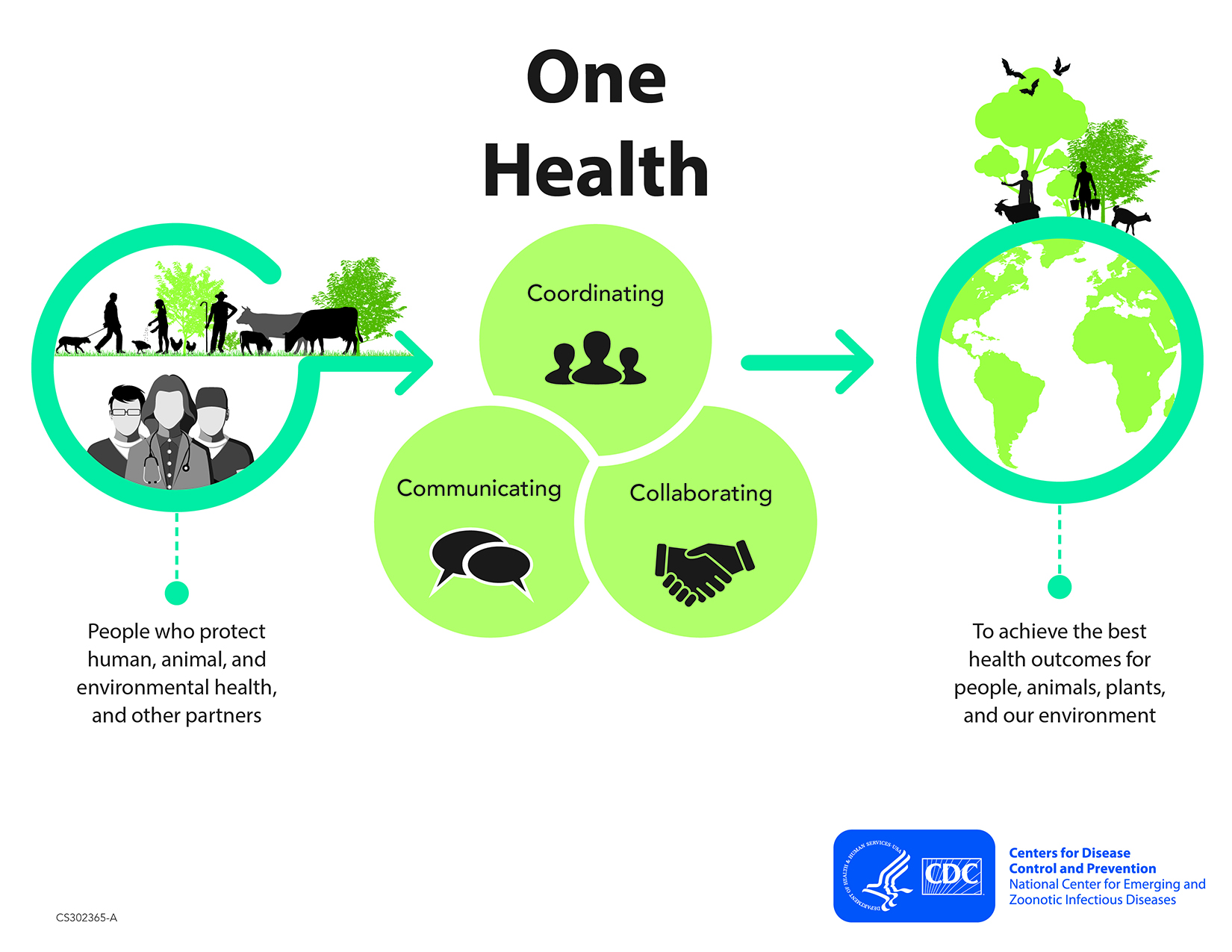
One Health Global Initiatives
In 2010, the United Nations and World Bank encouraged adopting the One Health approach in pandemic preparedness. This further emphasizes the importance of global adoption of the One Health approach, especially in light of the recent COVID-19 pandemic.
Therefore, the CDC One Health Office is taking a global step in creating a strategic, targeted approach to controlling and preventing infectious diseases. Projects such as workshops, collaborative research, and international discussions are held to improve global health conditions for people and animals. Eventually, the future of sustainable living conditions lies in leaving no one behind, including animals, plants, and the environment.
Kresentia Madina
Madina adalah Asisten Manajer Publikasi Digital di Green Network Asia. Ia adalah lulusan Program Studi Sastra Inggris dari Universitas Indonesia. Madina memiliki 3 tahun pengalaman profesional dalam publikasi digital internasional, program, dan kemitraan GNA, khususnya dalam isu-isu sosial dan budaya.

YOUR TITLE FOR CONDITION 1
YOUR BODY TEXT FOR CONDITION 1

 Test Custom Feature Image
Test Custom Feature Image  Electric Vehicles Roam the Roads of Kenya
Electric Vehicles Roam the Roads of Kenya  FedEx Engages Employees with Beach Clean-Up Initiative
FedEx Engages Employees with Beach Clean-Up Initiative  Come Back Stronger: Building Philippines’ Resilient Economy Post-COVID-19
Come Back Stronger: Building Philippines’ Resilient Economy Post-COVID-19  Inside Experian’s Sustainability Journey: An Interview with Chief Sustainability Officer Abigail Lovell
Inside Experian’s Sustainability Journey: An Interview with Chief Sustainability Officer Abigail Lovell  5 Food System Actors That Have Taken the 123 Pledge to Reduce Food Loss & Waste
5 Food System Actors That Have Taken the 123 Pledge to Reduce Food Loss & Waste  Test premium post
Test premium post